Associative array SystemVerilog
Table of Contents
- Associative array Stores entries in a sparse matrix
- Associative arrays allocate the storage only when it is used, unless like in the dynamic array we need to allocate memory before using it
- In associative array index expression is not restricted to integral expressions, but can be of any type
- An associative array implements a lookup table of the elements of its declared type. The data type to be used as an index serves as the lookup key and imposes an ordering
When the size of the collection is unknown or the data space is sparse, an associative array is a better option.
Dynamic arrays are useful for contiguous collections of variables whose number changes dynamically.
Array Declaration
data_type array_name [ index_type ];
where:
data_type – data type of the array elements.
array_name – name of the associative array.
index_type – data-type to be used as an index, or *.
* indicates the array is indexed by any integral expression of arbitrary size.
Array Example
int a_array1[*] ; // associative array of integer (unspecified index) bit [31:0] a_array2[string]; // associative array of 32-bit, indexed by string ev_array [myClass]; //associative array of event,indexed by class
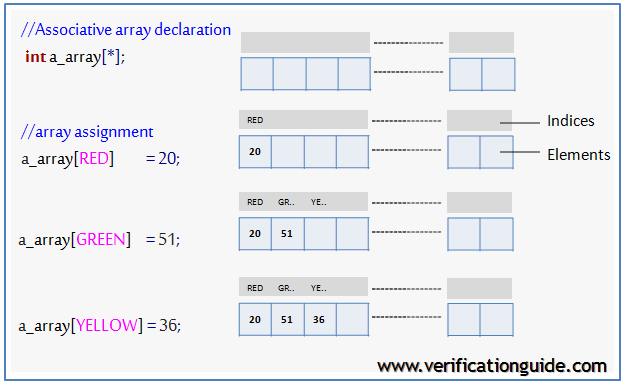
Associative Array Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| num() | returns the number of entries in the associative array |
| delete(index) | removes the entry at the specified index.exa_array.delete(index) |
| exists(index) | returns 1 if an element exists at the specified index else returns 0 |
| first(var) | assigns the value of first index to the variable var |
| last(var) | assigns the value of last index to the variable var |
| next(var) | assigns the value of next index to the variable var |
| prev(var) | assigns the value of previous index to the variable var |
Associative Array Examples
num(), first() and last() method’s
Example-1 : Associative Array Declaration, num(), first() and last() method’s.
module associative_array;
//array declaration
int a_array[*];
int index;
initial begin
//allocating array and assigning value to it
repeat(3) begin
a_array[index] = index*2;
index=index+4;
end
//num() –Associative array method
$display("\tNumber of entries in a_array is %0d",a_array.num());
$display("--- Associative array a_array entries and Values are ---");
foreach(a_array[i]) $display("\ta_array[%0d] \t = %0d",i,a_array[i]);
$display("--------------------------------------------------------");
//first()-Associative array method
a_array.first(index);
$display("\First entry is \t a_array[%0d] = %0d",index,a_array[index]);
//last()-Associative array method
a_array.last(index);
$display("\Last entry is \t a_array[%0d] = %0d",index,a_array[index]);
end
endmodule
Simulator Output:
Number of entries in a_array is 3 --- Associative array a_array entries and Values are --- a_array[0] = 0 a_array[4] = 8 a_array[8] = 16 -------------------------------------------------------- First entry is a_array[0] = 0 Last entry is a_array[8] = 16
exists(), prev() and last() method’s
Example-2 : Associative Array – exists(), prev() and last() method’s.
module associative_array;
//array declaration
int a_array[*];
int index;
initial begin
//allocating array and assigning value to it
repeat(3) begin
a_array[index] = index*2;
index=index+4;
end
//exists()-Associative array method
if(a_array.exists(8))
$display("Index 8 exists in a_array");
else
$display("Index 8 doesnt exists in a_array");
//last()-Associative array method
a_array.last(index);
$display("Last entry is a_array[%0d] = %0d",index,a_array[index]);
//prev()-Associative array method
a_array.prev(index);
$display("entry is a_array[%0d] = %0d",index,a_array[index]);
//next()-Associative array method
a_array.next(index);
$display("entry is a_array[%0d] = %0d",index,a_array[index]);
end
endmodule
Simulator Output:
Index 8 exists in a_array Last entry is a_array[8] = 16 entry is a_array[4] = 8 entry is a_array[8] = 16
bit and string index type
Example-3: Associative Array – bit and string index type.
module associative_array;
//array declaration
int a_array1[bit [7:0]]; //index type is bit [7:0] and entry type is int
bit a_array2[string] ; //index type is string and entry type is bit
initial begin
//allocating array and assigning value to it
a_array1[5] = 10;
a_array1[8] = 20;
a_array2["GOOD_PKT"] = 1;
a_array2["BAD_PKT"] = 0;
foreach(a_array1[index])
$display("a_array1[%0d] = %0d",index,a_array1[index]);
foreach(a_array2[index])
$display("a_array2[%0s] = %0d",index,a_array2[index]);
end
endmodule
Simulator Output:
a_array1[5] = 10 a_array1[8] = 20 a_array2[BAD_PKT] = 0 a_array2[GOOD_PKT] = 1
Deleting complete Assoc Array
Example-4: Deleting complete Associative Array
Calling array.delete() method will delete the complete array, which leads to the deletion of all the entries of an array.
module associative_array;
//array declaration
int a_array[*];
int index;
initial begin
//allocating array and assigning value to it
repeat(3) begin
a_array[index] = index*2;
index=index+4;
end
$display("[Before-Delete] Associative array size is %0d",a_array.size());
a_array.delete();
$display("[After -Delete] Associative array size is %0d",a_array.size());
end
endmodule
Simulator Output:
[Before-Delete] Associative array size is 3 [After -Delete] Associative array size is 0
