Packed and Unpacked array in SystemVerilog
Table of Contents
- The term packed array is used to refer to the dimensions declared before the data identifier name
- The term unpacked array is used to refer to the dimensions declared after the data identifier name
bit [7:0] temp_var; // packed array of bit types bit temp_var [7:0]; // unpacked array of real types
Packed array
- Packed arrays can be of single bit data types (reg, logic, bit), enumerated types, and recursively packed arrays and packed structures
- One dimensional packed array is referred to as a vector
- Vector: A vector is a multi-bit data object of reg/logic/bit declared by specifying a range
- Scalar: Scalar is 1-bit data object of reg/logic/bit declared without specifying a range
- A packed array is a mechanism for subdividing a vector into sub-fields, which can be conveniently accessed as array elements.
- A packed array is guaranteed to be represented as a contiguous set of bits.
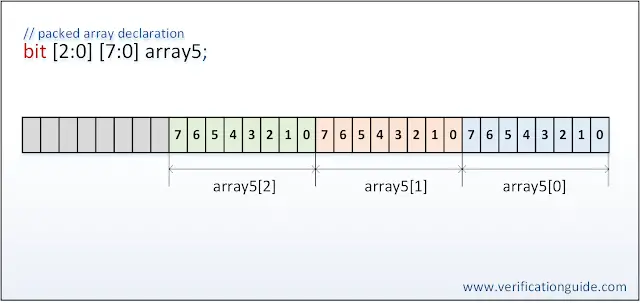
Packed array example
bit [2:0] [7:0] array5;
The below diagram shows storing packed array as a contiguous set of bits.
UnPacked array
- Unpacked arrays can be of any data type.
- Unpacked arrays shall be declared by specifying the element ranges after the identifier name.
- An unpacked array may or may not be so represented as a contiguous set of bits.
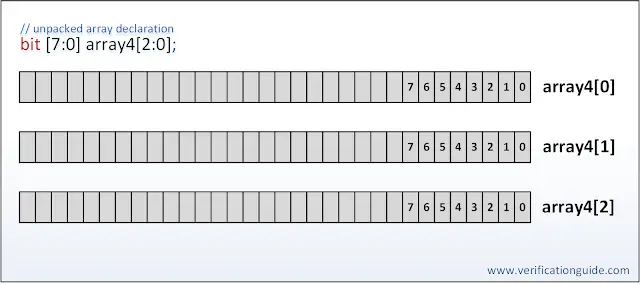
Unpacked array example
bit [7:0] array4[2:0];
Below diagram shows storing unpacked array as a non-contiguous set of bits.