How to write uvm sequence
Table of Contents
A sequence generates a series of sequence_item’s and sends it to the driver via sequencer, Sequence is written by extending the uvm_sequence.

- A uvm_sequence is derived from an uvm_sequence_item
- a sequence is parameterized with the type of sequence_item, this defines the type of the item sequence that will send/receive to/from the driver.
sequence base class
virtual class uvm_sequence #( type REQ = uvm_sequence_item,
type RSP = REQ ) extends uvm_sequence_base
example:
class write_sequence extends uvm_sequence #(mem_seq_item); .... .... endclass
the sequence has handle req and rsp of mem_seq_item.
request/req:
A transaction that provides information to initiate the processing of a particular operation.
response/rsp:
A transaction that provides information about the completion or status of a particular operation.
Sequence Execution
Most important properties of a sequence are,
- body method
- m_sequencer handle
body Method:
body method defines, what the sequence does.
m_sequencer Handle:
The m_sequencer handle contains the reference to the sequencer on which the sequence is running.
The sequence will get executed upon calling the start of the sequence from the test.
sequence_name.start(sequencer_name);
sequencer_name specifies on which sequencer sequence has to run.
- There are Methods, macros and pre-defined callbacks associated with uvm_sequence.
- Users can define the methods(task or function) to pre-defined callbacks. these methods will get executed automatically upon calling the start of the sequence.
- These methods should not be called directly by the user.
Below block diagram shows the order in which the methods will get called on calling the start of a sequence.
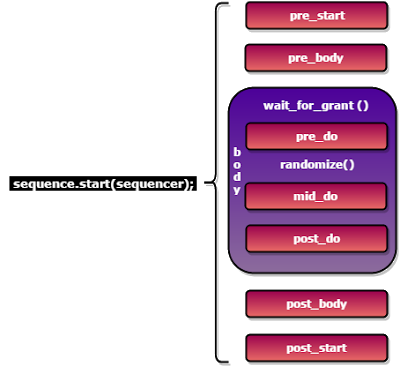
* mid_do and post_do are functions, All other are tasks
Starting The Sequence:
Logic to generate and send the sequence_item will be written inside the body() method of the sequence.
The handshake between the sequence, sequencer and driver to send the sequence_item is given below.
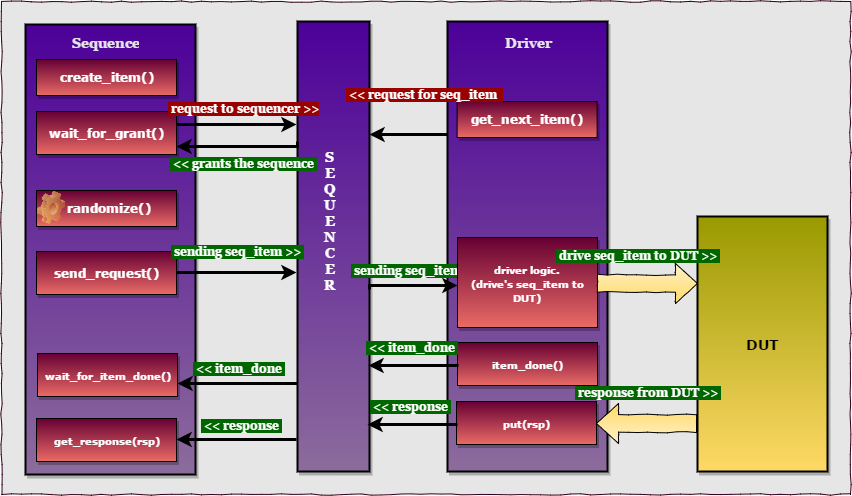
Communication between the Sequence and driver involves below steps,
1.create_item() / create req.
2.wait_for_grant().
3.randomize the req.
4.send the req.
5.wait for item done.
6.get response.
* Step 5 and 6 are optional.
| Method Call | Description |
|---|---|
| create_item() req = **_seq_item::type_id::create(“req”); |
Create and initialize* a sequence_item or sequence *initialize – initialized to communicate with the specified sequencer |
| wait_for_grant() | This method call is blocking, Execution will be blocked until the method returns. 1.This method issues a request to the current sequencer 2.The sequencer grants on getting get_next_item() request from driver |
| req.randomize() | This method is to randomize the sequence_item |
| send_request(req,re-randomize) re-randomize = 0 or re-randomize = 1; |
Send the request item to the sequencer, which will forward it to the driver. If the re-randomize the bit is set, the item will be randomized before being sent to the driver. |
| wait_for_item_done() | This call is optional. This task will block until the driver calls item_done or put. |
| get_current_item() | Returns the request item currently being executed by the sequencer. If the sequencer is not currently executing an item, this method will return null. |
| get_response(rsp) | receives the response from driver. |
Writing UVM Sequence
class mem_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(mem_sequence)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "mem_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
req = mem_seq_item::type_id::create("req"); //create the req (seq item)
wait_for_grant(); //wait for grant
assert(req.randomize()); //randomize the req
send_request(req); //send req to driver
wait_for_item_done(); //wait for item done from driver
get_response(rsp); //get response from driver
endtask
endclass
Note: assert(req.randomize());, will return the assertion error on randomization failure.
UVM Sequence macros
These macros are used to start sequences and sequence items on default sequencer, m_sequencer.
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
| `uvm_do(Item/Seq) | This macro takes seq_item or sequence as argument. On calling `uvm_do() the above-defined 6 steps will be executed. |
| `uvm_create(Item/Seq) | This macro creates the item or sequence. |
| `uvm_send(Item/Seq) | create() and randomize() are skipped, rest all other steps are executed. |
| `uvm_rand_send(Item/Seq) | Only create() is skipped, rest all other steps are executed. |
| `uvm_do_with(Item/Seq,Constraints) | This macro performs above 6 steps along with constraints defined in second argument. |
| `uvm_rand_send_with(Item/Seq,Constraints) | create() is skipped, rest all other steps are executed along with constraints defined in second argument. |
| `uvm_do_pri(Item/Seq,Priority ) | Performs `uvm_do() with priority mentioned. |
| `uvm_do_pri_with(Item/Seq,Constraints,Priority) | Performs `uvm_do() along with constraints defined and priority mentioned. |
| `uvm_send_pri(Item/Seq,Priority) | create() and randomize() are skipped, rest all other steps are executed with priority mentioned. |
| `uvm_rand_send_pri(Item/Seq,Priority) | Only create() is skipped, rest all other steps are executed with priority mentioned. |
| `uvm_rand_send_pri_with(Item/Seq,Priority, Constraints) | create() is skipped, rest all other steps are executed along with constraints defined with priority mentioned. |
| `uvm_declare_p_sequencer(SEQUENCER) | This macro is used to declare a variable p_sequencer whose type is specified by SEQUENCER. by using p_sequencer handle, properties of sequencer can be accessed. |
Writing the sequence using Macro’s
`uvm_do()
class mem_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(mem_sequence)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "mem_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
`uvm_do(req)
endtask
endclass
`uvm_create() and `uvm_send()
class mem_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(mem_sequence)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "mem_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
`uvm_create(req)
assert(req.randomize());
`uvm_send(req);
endtask
endclass
`uvm_rand_send()
class mem_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(mem_sequence)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "mem_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
`uvm_create(req)
`uvm_rand_send(req)
endtask
endclass
`uvm_do_with()
class write_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(write_sequence)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "write_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
`uvm_do_with(req,{req.wr_en == 1;})
endtask
endclass
`uvm_rand_send_with()
class read_sequence extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
`uvm_object_utils(read_sequence)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "read_sequence");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
`uvm_create(req)
`uvm_rand_send_with(req,{req.rd_en == 1;})
endtask
endclass
Calling sequence’s inside the sequence
class wr_rd_seq extends uvm_sequence#(mem_seq_item);
write_sequence wr_seq;
read_sequence rd_seq;
`uvm_object_utils(wr_rd_seq)
//Constructor
function new(string name = "wr_rd_seq");
super.new(name);
endfunction
virtual task body();
`uvm_do(wr_seq)
`uvm_do(rd_seq)
endtask
endclass
difference between m_sequencer and p_sequencer:
m_sequencer,
The m_sequencer handle contains the reference to the sequencer(default sequencer) on which the sequence is running.
This is determined by,
- the sequencer handle provided in the start method
- the sequencer used by the parent sequence
- the sequencer that was set using the set_sequencer method
p_sequencer,
The p_sequencer is a variable, used as a handle to access the sequencer properties.
p_sequencer is defined using the macro `uvm_declare_p_sequencer(SEQUENCER_NAME)
❮ Previous Next ❯