Category: SystemVerilog Examples
SystemVerilog Code Library
- Sample Data based on Strobe – Click here
- Print the Current Line number in SystemVerilog – Click here
- Generating weighted random number – Click here
- Dword array to Byte array assignment – Click here or 32bit to 8 bit array
SystemVerilog TestBench Example 01
Memory Model TestBench Without Monitor, Agent, and Scoreboard
TestBench Architecture
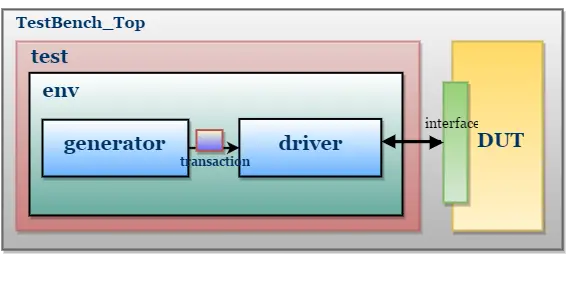
Transaction Class
- Fields required to generate the stimulus are declared in the transaction class
- Transaction class can also be used as a placeholder for the activity monitored by the monitor on DUT signals
- So, the first step is to declare the
Fields‘ in the transaction class - Below are the steps to write a transaction class
1. Declaring the fields.
class transaction; //declaring the transaction items bit [1:0] addr; bit wr_en; bit rd_en; bit [7:0] wdata; bit [7:0] rdata; bit [1:0] cnt; endclass
2. To generate the random stimulus, declare the fields as rand.
class transaction;
//declaring the transaction items
rand bit [1:0] addr;
rand bit wr_en;
rand bit rd_en;
rand bit [7:0] wdata;
bit [7:0] rdata;
bit [1:0] cnt;
endclass
3. Either write or read operation will be performed at once, so wr_en or rd_en is generated by adding constraint.
class transaction;
//declaring the transaction items
rand bit [1:0] addr;
rand bit wr_en;
rand bit rd_en;
rand bit [7:0] wdata;
bit [7:0] rdata;
bit [1:0] cnt;
//constaint, to generate any one among write and read
constraint wr_rd_c { wr_en != rd_en; };
endclass
Generator Class
Generator class is responsible for,
- Generating the stimulus by randomizing the transaction class
- Sending the randomized class to driver
class generator; ------ endclass
1. Declare the transaction class handle,
class generator; //declaring transaction class rand transaction trans; endclass
2. Randomize the transaction class,
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
endtask
endclass
3. Mailbox is used to send the randomized transaction to Driver,
This involves,
- Declaring the Mailbox
- Getting the Mailbox handle from the env class. ( because the same mailbox will be shared across generator and driver)
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//declaring mailbox
mailbox gen2driv;
//constructor
function new(mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the mailbox handle from env
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
endtask
endclass
4. Adding a variable to control the number of packets to be created,
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//declaring mailbox
mailbox gen2driv;
//repeat count, to specify number of items to generate
int repeat_count;
//constructor
function new(mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the mailbox handle from env
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the repeat_count number of transaction packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
repeat(repeat_count) begin
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
end
endtask
endclass
5. Adding an event to indicate the completion of the generation process, the event will be triggered on the completion of the Generation process.
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//declaring mailbox
mailbox gen2driv;
//repeat count, to specify number of items to generate
int repeat_count;
//event
event ended;
//constructor
function new(mailbox gen2driv,event ended);
//getting the mailbox handle from env
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
this.ended = ended;
endfunction
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the repeat_count number of transaction packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
repeat(repeat_count) begin
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
end
-> ended;
endtask
endclass
Interface:
Interface will group the signals, specifies the direction (Modport) and Synchronize the signals(Clocking Block).
interface mem_intf(input logic clk,reset); ---- endinterface
1. Driver Clocking Block,
//driver clocking block
clocking driver_cb @(posedge clk);
default input #1 output #1;
output addr;
output wr_en;
output rd_en;
output wdata;
input rdata;
endclocking
2. Monitor Clocking Block,
//monitor clocking block
clocking monitor_cb @(posedge clk);
default input #1 output #1;
input addr;
input wr_en;
input rd_en;
input wdata;
input rdata;
endclocking
3. Driver and Monitor modport,
//driver modport modport DRIVER (clocking driver_cb,input clk,reset); //monitor modport modport MONITOR (clocking monitor_cb,input clk,reset);
4. Complete Interface code,
interface mem_intf(input logic clk,reset);
//declaring the signals
logic [1:0] addr;
logic wr_en;
logic rd_en;
logic [7:0] wdata;
logic [7:0] rdata;
//driver clocking block
clocking driver_cb @(posedge clk);
default input #1 output #1;
output addr;
output wr_en;
output rd_en;
output wdata;
input rdata;
endclocking
//monitor clocking block
clocking monitor_cb @(posedge clk);
default input #1 output #1;
input addr;
input wr_en;
input rd_en;
input wdata;
input rdata;
endclocking
//driver modport
modport DRIVER (clocking driver_cb,input clk,reset);
//monitor modport
modport MONITOR (clocking monitor_cb,input clk,reset);
endinterface
Driver Class
Driver class is responsible for,
- receive the stimulus generated from the generator and drive to DUT by assigning transaction class values to interface signals.
class driver; ---- endclass
1. Declare interface and mailbox, Get the interface and mailbox handle through the constructor
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox gen2driv;
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif,mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the interface
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//getting the mailbox handle from environment
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
2. Adding a reset task, which initializes the Interface signals to default values
For simplicity, define is used to access interface signals.
`define DRIV_IF mem_vif.DRIVER.driver_cb
`DRIV_IF will point to mem_vif.DRIVER.driver_cb
//Reset task, Reset the Interface signals to default/initial values
task reset;
wait(mem_vif.reset);
$display("--------- [DRIVER] Reset Started ---------");
`DRIV_IF.wr_en <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.addr <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.wdata <= 0;
wait(!mem_vif.reset);
$display("--------- [DRIVER] Reset Ended ---------");
endtask
3. Adding a drive task to drive the transaction packet to the interface signal
//drive the transaction items to interface signals
task drive;
forever begin
transaction trans;
`DRIV_IF.wr_en <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0;
gen2driv.get(trans);
$display("--------- [DRIVER-TRANSFER: %0d] ---------",no_transactions);
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
`DRIV_IF.addr <= trans.addr;
if(trans.wr_en) begin
`DRIV_IF.wr_en <= trans.wr_en;
`DRIV_IF.wdata <= trans.wdata;
$display("\tADDR = %0h \tWDATA = %0h",trans.addr,trans.wdata);
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
end
if(trans.rd_en) begin
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= trans.rd_en;
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0;
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
trans.rdata = `DRIV_IF.rdata;
$display("\tADDR = %0h \tRDATA = %0h",trans.addr,`DRIV_IF.rdata);
end
$display("-----------------------------------------");
no_transactions++;
end
endtask
4. Adding a local variable to track the number of packets driven, and increment the variable in drive task
(This
will be useful to end the test-case/Simulation. i.e compare the
generated pkt’s and driven pkt’s, if both are same then end the
simulation)
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//drive the transaction items to interface signals
task drive;
------
------
no_transactions++;
endtask
5. Complete driver code.
class driver;
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox gen2driv;
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif,mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the interface
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//getting the mailbox handle from environment
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//Reset task, Reset the Interface signals to default/initial values
task reset;
wait(mem_vif.reset);
$display("--------- [DRIVER] Reset Started ---------");
`DRIV_IF.wr_en <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.addr <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.wdata <= 0;
wait(!mem_vif.reset);
$display("--------- [DRIVER] Reset Ended---------");
endtask
//drive the transaction items to interface signals
task drive;
forever begin
transaction trans;
`DRIV_IF.wr_en <= 0;
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0;
gen2driv.get(trans);
$display("--------- [DRIVER-TRANSFER: %0d] ---------",no_transactions);
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
`DRIV_IF.addr <= trans.addr;
if(trans.wr_en) begin
`DRIV_IF.wr_en <= trans.wr_en;
`DRIV_IF.wdata <= trans.wdata;
$display("\tADDR = %0h \tWDATA = %0h",trans.addr,trans.wdata);
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
end
if(trans.rd_en) begin
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= trans.rd_en;
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
`DRIV_IF.rd_en <= 0;
@(posedge mem_vif.DRIVER.clk);
trans.rdata = `DRIV_IF.rdata;
$display("\tADDR = %0h \tRDATA = %0h",trans.addr,`DRIV_IF.rdata);
end
$display("-----------------------------------------");
no_transactions++;
end
endtask
endclass
Environment
Environment is container class contains Mailbox, Generator and Driver.
Creates the mailbox, generator and driver shares the mailbox handle across the Generator and Driver.
class environment; --- endclass
1. Declare the handles,
//generator and driver instance generator gen; driver driv; //mailbox handle's mailbox gen2driv; //event for synchronization between generator and test event gen_ended; //virtual interface virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
2. In Construct Method, Create
- Mailbox
- Generator
- Driver
and pass the interface handle through the new() method.
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif);
//get the interface from test
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv,gen_ended);
driv = new(mem_vif,gen2driv);
endfunction
3. For better accessibility.
Generator and Driver activity can be divided and controlled in three methods.
- pre_test() – Method to call Initialization. i.e, reset method.
- test() – Method to call Stimulus Generation and Stimulus Driving.
- post_test() – Method to wait the completion of generation and driving.
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen_ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
endtask
4. Add a run task to call the above methods,
call $finish after post_test() to end the simulation.
task run;
pre_test();
test();
post_test();
$finish;
endtask
5. Complete environment class code.
`include "transaction.sv"
`include "generator.sv"
`include "driver.sv"
class environment;
//generator and driver instance
generator gen;
driver driv;
//mailbox handle's
mailbox gen2driv;
//event for synchronization between generator and test
event gen_ended;
//virtual interface
virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif);
//get the interface from test
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv,gen_ended);
driv = new(mem_vif,gen2driv);
endfunction
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen_ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
endtask
//run task
task run;
pre_test();
test();
post_test();
$finish;
endtask
endclass
Test
Test code is written with the program block.
The test is responsible for,
- Creating the environment.
- Configuring the testbench i.e, setting the type and number of transactions to be generated.
- Initiating the stimulus driving.
program test; ---- endprogram
1. Declare and Create an environment,
//declaring environment instance
environment env;
initial begin
//creating environment
env = new(intf);
end
2. Configure the number of transactions to be generated,
//setting the repeat count of generator as 10, means to generate 10 packets
env.gen.repeat_count = 10;
3. Initiating the stimulus driving,
//calling run of env, it interns calls generator and driver main tasks.
env.run();
4. Complete Test Code,
`include "environment.sv"
program test(mem_intf intf);
//declaring environment instance
environment env;
initial begin
//creating environment
env = new(intf);
//setting the repeat count of generator as 10, means to generate 10 packets
env.gen.repeat_count = 10;
//calling run of env, it interns calls generator and driver main tasks.
env.run();
end
endprogram
TestBench Top
- This is the topmost file, which connects the DUT and TestBench.
- TestBench top consists of DUT, Test and Interface instances.
- The interface connects the DUT and TestBench.
module tbench_top; --- endmodule
1. Declare and Generate the clock and reset,
//clock and reset signal declaration
bit clk;
bit reset;
//clock generation
always #5 clk = ~clk;
//reset Generation
initial begin
reset = 1;
#5 reset =0;
end
2. Create Interface instance,
//creatinng instance of interface, inorder to connect DUT and testcase mem_intf intf(clk,reset);
3. Create Design Instance and Connect Interface signals,
//DUT instance, interface signals are connected to the DUT ports
memory DUT (
.clk(intf.clk),
.reset(intf.reset),
.addr(intf.addr),
.wr_en(intf.wr_en),
.rd_en(intf.rd_en),
.wdata(intf.wdata),
.rdata(intf.rdata)
);
4. Create a test instance and Pass the interface handle,
//Testcase instance, interface handle is passed to test as an argument test t1(intf);
5. Add logic to generate the dump,
initial begin
$dumpfile("dump.vcd"); $dumpvars;
end
6. Complete testbench top code,
`include "interface.sv"
`include "random_test.sv"
module tbench_top;
//clock and reset signal declaration
bit clk;
bit reset;
//clock generation
always #5 clk = ~clk;
//reset Generation
initial begin
reset = 1;
#5 reset =0;
end
//creatinng instance of interface, inorder to connect DUT and testcase
mem_intf intf(clk,reset);
//Testcase instance, interface handle is passed to test as an argument
test t1(intf);
//DUT instance, interface signals are connected to the DUT ports
memory DUT (
.clk(intf.clk),
.reset(intf.reset),
.addr(intf.addr),
.wr_en(intf.wr_en),
.rd_en(intf.rd_en),
.wdata(intf.wdata),
.rdata(intf.rdata)
);
//enabling the wave dump
initial begin
$dumpfile("dump.vcd"); $dumpvars;
end
endmodule
Edit and Execute the Memory Model TestBench code in EDA Playground.
SystemVerilog TestBench Example – Memory
Memory Model TestBench With Monitor and Scoreboard
TestBench Architecture:
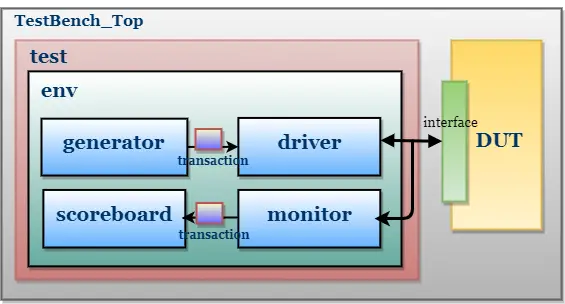
Only monitor and scoreboard are explained here, Refer to ‘Memory Model’ TestBench Without Monitor, Agent, and Scoreboard for other components.
Monitor
- Samples the interface signals and converts the signal level activity to the transaction level
- Send the sampled transaction to Scoreboard via Mailbox
- Below are the steps to write a monitor
1. Writing monitor class.
class monitor; ------ endclass
2. Declare interface and mailbox, Get the interface and mailbox handle through the constructor.
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif,mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the interface
this.vif = vif;
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
3. Sampling logic and sending the sampled transaction to the scoreboard
task main;
forever begin
transaction trans;
trans = new();
@(posedge mem_vif.MONITOR.clk);
wait(`MON_IF.rd_en || `MON_IF.wr_en);
trans.addr = `MON_IF.addr;
trans.wr_en = `MON_IF.wr_en;
trans.wdata = `MON_IF.wdata;
if(`MON_IF.rd_en) begin
trans.rd_en = `MON_IF.rd_en;
@(posedge mem_vif.MONITOR.clk);
@(posedge mem_vif.MONITOR.clk);
trans.rdata = `MON_IF.rdata;
end
mon2scb.put(trans);
end
endtask
4. Complete monitor code.
`define MON_IF mem_vif.MONITOR.monitor_cb
class monitor;
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif,mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the interface
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
//Samples the interface signal and send the sample packet to scoreboard
task main;
forever begin
transaction trans;
trans = new();
@(posedge mem_vif.MONITOR.clk);
wait(`MON_IF.rd_en || `MON_IF.wr_en);
trans.addr = `MON_IF.addr;
trans.wr_en = `MON_IF.wr_en;
trans.wdata = `MON_IF.wdata;
if(`MON_IF.rd_en) begin
trans.rd_en = `MON_IF.rd_en;
@(posedge mem_vif.MONITOR.clk);
@(posedge mem_vif.MONITOR.clk);
trans.rdata = `MON_IF.rdata;
end
mon2scb.put(trans);
end
endtask
endclass
Scoreboard
Scoreboard receives the sampled packet from monitor,
- if the transaction type is “read”, compares the read data with the local memory data
- if the transaction type is “write”, local memory will be written with the wdata
class scoreboard; ------ endclass
1. Declaring the mailbox and variable to keep count of transactions, connecting handle through the constructor,
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//constructor
function new(mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
2. logic to store wdata and compare rdata with stored data,
//stores wdata and compare rdata with stored data
task main;
transaction trans;
forever begin
#50;
mon2scb.get(trans);
if(trans.rd_en) begin
if(mem[trans.addr] != trans.rdata)
$error("[SCB-FAIL] Addr = %0h,\n \t Data :: Expected = %0h Actual = %0h",trans.addr,mem[trans.addr],trans.rdata);
else
$display("[SCB-PASS] Addr = %0h,\n \t Data :: Expected = %0h Actual = %0h",trans.addr,mem[trans.addr],trans.rdata);
end
else if(trans.wr_en)
mem[trans.addr] = trans.wdata;
no_transactions++;
end
endtask
3. Complete scoreboard code.
class scoreboard;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//array to use as local memory
bit [7:0] mem[4];
//constructor
function new(mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
foreach(mem[i]) mem[i] = 8'hFF;
endfunction
//stores wdata and compare rdata with stored data
task main;
transaction trans;
forever begin
#50;
mon2scb.get(trans);
if(trans.rd_en) begin
if(mem[trans.addr] != trans.rdata)
$error("[SCB-FAIL] Addr = %0h,\n \t Data :: Expected = %0h Actual = %0h",trans.addr,mem[trans.addr],trans.rdata);
else
$display("[SCB-PASS] Addr = %0h,\n \t Data :: Expected = %0h Actual = %0h",trans.addr,mem[trans.addr],trans.rdata);
end
else if(trans.wr_en)
mem[trans.addr] = trans.wdata;
no_transactions++;
end
endtask
endclass
Environment
Here only updates are mentioned. i.e adding monitor and scoreboard to the previous example.
1. Declare the handles,
//generator and driver instance generator gen; driver driv; monitor mon; //---NEW CODE--- scoreboard scb; //---NEW CODE--- //mailbox handle's mailbox gen2driv; mailbox mon2scb; //---NEW CODE--- //virtual interface virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
2. In Construct Method, Create
- Mailbox (mon2scb)
- Monitor
- Scoreboard
and pass the interface handle through the new() method.
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif);
//get the interface from test
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
mon2scb = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv,gen_ended);
driv = new(mem_vif,gen2driv);
mon = new(mem_vif,mon2scb);
scb = new(mon2scb);
endfunction
3. Calling monitor and scoreboard tasks,
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
mon.main(); //---NEW CODE---
scb.main(); //---NEW CODE---
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen.ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
wait(gen.repeat_count == scb.no_transactions); //---NEW CODE--- endtask
4. Complete environment class code,
class environment;
//generator and driver instance
generator gen;
driver driv;
monitor mon;
scoreboard scb;
//mailbox handle's
mailbox gen2driv;
mailbox mon2scb;
//event for synchronization between generator and test
event gen_ended;
//virtual interface
virtual mem_intf mem_vif;
//constructor
function new(virtual mem_intf mem_vif);
//get the interface from test
this.mem_vif = mem_vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
mon2scb = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv,gen_ended);
driv = new(mem_vif,gen2driv);
mon = new(mem_vif,mon2scb);
scb = new(mon2scb);
endfunction
//
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
mon.main();
scb.main();
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen_ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
wait(gen.repeat_count == scb.no_transactions);
endtask
//run task
task run;
pre_test();
test();
post_test();
$finish;
endtask
endclass
Edit and Execute Memory Model TestBench code in EDA Playground.
SystemVerilog TestBench Example — Memory_M
SystemVerilog Verification Environment/TestBench for Memory Model
The steps involved in the verification process are,
- Creation of Verification plan
- Testbench Architecture
- Writing TestBench
Before writing/creating the verification plan need to know about design, so will go through the design specification.
* In this example Design/DUT is Memory Model.
Memory Model Design Specification
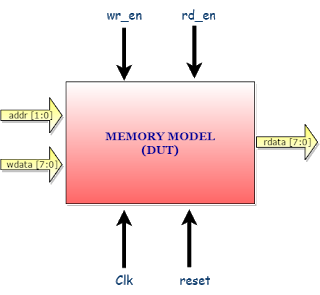
Signal Definition:
| Signal Name | Direction wrt to Design | Description |
|---|---|---|
| clk | input | clock signal |
| reset | input | reset signal |
| addr[1:0] | input | Address signal on which the address is specified |
| wr_en | input | write enable signal, indicates the write operation |
| rd_en | input | read enable signal, indicates the read operation |
| wdata[7:0] | input | wdata signal for write data |
| rdata[7:0] | output | rdata signal for read data |
Operations:
Write Operation:
address, wr_en, and wdata should be driven at the same clock cycle.
Read Operation:
address and rd_en should be driven on the same clock cycle, Design will respond with the data in the next clock cycle.
Design Features,
- The Memory model is capable of storing 8bits of data per address location
- Reset values of each address memory location is ‘hFF
Creation of Verification plan
The verification plan is the list of scenarios need to be verified.
let’s list the few scenarios,
- Write and Read to a particular memory location
- Perform write to any memory location, read from the same memory location, read data should be the same as written data
- Write and Read to all memory locations
- Perform write and read to all the memory locations (as the address is 2bit width the possible address are 2‘b00, 2’b01, 2’b10, and 2’b11)
- Default memory value check
- Check default memory values. (before writing any locations, do read operation we should get default values as ‘hFF)
- Reset in Middle of Write/Read Operation
- Assert reset in between write/read operation and check for default values. (after writing to few locations assert the reset and perform read operation, we should get default memory location value ‘hFF)
TestBench Hierarchy and Architecture
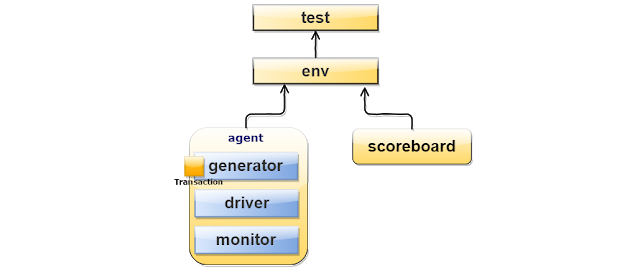
Writing Verification Environment/TestBench
For simplicity will write the two Testbenches,
SystemVerilog TestBench Example – ADDER
‘ADDER’ TestBench Without Monitor, Agent and Scoreboard
TestBench Architecture

Transaction Class
- Fields required to generate the stimulus are declared in the transaction class.
- Transaction class can also be used as a placeholder for the activity monitored by the monitor on DUT signals.
- So, the first step is to declare the ‘Fields‘ in the transaction class.
- Below are the steps to write the transaction class.
1. Declaring the fields.
class transaction; //declaring the transaction items bit [3:0] a; bit [3:0] b; bit [6:0] c; endclass
2. To generate the random stimulus, declare the fields as ‘rand‘.
class transaction;
//declaring the transaction items
rand bit [3:0] a;
rand bit [3:0] b;
bit [7:0] c;
endclass
3. Adding display() method to display Transaction properties.
class transaction;
//declaring the transaction items
rand bit [3:0] a;
rand bit [3:0] b;
bit [6:0] c;
function void display(string name);
$display("-------------------------");
$display("- %s ",name);
$display("-------------------------");
$display("- a = %0d, b = %0d",a,b);
$display("- c = %0d",c);
$display("-------------------------");
endfunction
endclass
Generator Class
Generator class is responsible for,
- Generating the stimulus by randomizing the transaction class
- Sending the randomized class to driver
class generator; ------ endclass
1. Declare the transaction class handle,
class generator; //declaring transaction class rand transaction trans; endclass
2. ‘Randomize’ the transaction class,
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
endtask
endclass
3. Adding Mailbox and event,
Mailbox is used to send the randomized transaction to Driver.
Event to indicate the end of packet generation.
This involves,
- Declaring the Mailbox and Event
- Getting the Mailbox handle from the env class ( because the same mailbox will be shared across generator and driver).
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//declaring mailbox
mailbox gen2driv;
//event, to indicate the end of transaction generation
event ended;
//constructor
function new(mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the mailbox handle from env
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
-> ended; //triggering indicatesthe end of generation
endtask
endclass
4. Adding a variable to control the number of packets to be created,
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//declaring mailbox
mailbox gen2driv;
//event, to indicate the end of transaction generation
event ended;
//repeat count, to specify number of items to generate
int repeat_count;
//constructor
function new(mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the mailbox handle from env
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the repeat_count number of transaction packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
repeat(repeat_count) begin
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
end
-> ended; //triggering indicatesthe end of generation
endtask
endclass
5. Adding an event to indicate the completion of the generation process, the event will be triggered on the completion of the Generation process.
class generator;
//declaring transaction class
rand transaction trans;
//declaring mailbox
mailbox gen2driv;
//repeat count, to specify number of items to generate
int repeat_count;
//event, to indicate the end of transaction generation
event ended;
//constructor
function new(mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the mailbox handle from env
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//main task, generates(create and randomizes) the repeat_count number of transaction packets and puts into mailbox
task main();
repeat(repeat_count) begin
trans = new();
if( !trans.randomize() ) $fatal("Gen:: trans randomization failed");
gen2driv.put(trans);
end
-> ended; //triggering indicatesthe end of generation
endtask
endclass
Interface
Interface will group the signals.
This is a simple interface without modport and clocking block.
interface intf(input logic clk,reset); ---- endinterface
1. Complete Interface code,
interface intf(input logic clk,reset); //declaring the signals logic valid; logic [3:0] a; logic [3:0] b; logic [6:0] c; endinterface
Driver Class
Driver class is responsible for,
- receive the stimulus generated from the generator and drive to DUT by assigning transaction class values to interface signals.
class driver; ---- endclass
1. Declare interface and mailbox, Get the interface and mailbox handle through a constructor.
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual intf vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox gen2driv;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif,mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the interface
this.vif = vif;
//getting the mailbox handle from environment
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
2. Adding a reset task, which initializes the Interface signals to default values.
//Reset task, Reset the Interface signals to default/initial values
task reset;
wait(vif.reset);
$display("[ DRIVER ] ----- Reset Started -----");
vif.a <= 0;
vif.b <= 0;
vif.valid <= 0;
wait(!vif.reset);
$display("[ DRIVER ] ----- Reset Ended -----");
endtask
3. Adding a drive task to drive the transaction packet to the interface signal.
//drive the transaction items to interface signals
task drive;
transaction trans;
gen2driv.get(trans);
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 1;
vif.a <= trans.a;
vif.b <= trans.b;
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 0;
trans.c <= vif.c;
@(posedge vif.clk);
trans.display("[ Driver ]");
no_transactions++;
end
endtask
4. Adding a local variable to track the number of packets driven, and increment the variable in the drive task.
(This
will be useful to end the test-case/Simulation. i.e compare the
generated pkt’s and driven pkt’s if both are same then end the
simulation)
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//drive the transaction items to interface signals
task drive;
------
------
no_transactions++;
endtask
5. Complete driver code.
class driver;
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual intf vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox gen2driv;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif,mailbox gen2driv);
//getting the interface
this.vif = vif;
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.gen2driv = gen2driv;
endfunction
//Reset task, Reset the Interface signals to default/initial values
task reset;
wait(vif.reset);
$display("[ DRIVER ] ----- Reset Started -----");
vif.a <= 0;
vif.b <= 0;
vif.valid <= 0;
wait(!vif.reset);
$display("[ DRIVER ] ----- Reset Ended -----");
endtask
//drivers the transaction items to interface signals
task main;
forever begin
transaction trans;
gen2driv.get(trans);
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 1;
vif.a <= trans.a;
vif.b <= trans.b;
@(posedge vif.clk);
vif.valid <= 0;
trans.c <= vif.c;
@(posedge vif.clk);
trans.display("[ Driver ]");
no_transactions++;
end
endtask
endclass
Environment
Environment is container class contains Mailbox, Generator and Driver.
Creates the mailbox, generator and driver shares the mailbox handle across the Generator and Driver.
class environment; --- endclass
1. Declare the handles,
//generator and driver instance generator gen; driver driv; //mailbox handle's mailbox gen2driv; //virtual interface virtual intf vif;
2. In Construct Method, Create
- Mailbox
- Generator
- Driver
and pass the interface handle through the new() method.
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif);
//get the interface from test
this.vif = vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv);
driv = new(vif,gen2driv);
endfunction
3. For better accessibility.
Generator and Driver activity can be divided and controlled in three methods.
- pre_test() – Method to call Initialization. i.e, reset method.
- test() – Method to call Stimulus Generation and Stimulus Driving.
- post_test() – Method to wait the completion of generation and driving.
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen.ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
endtask
4. Add a run task to call the above methods,
call $finish after post_test() to end the simulation.
task run;
pre_test();
test();
post_test();
$finish;
endtask
5. Complete environment class code.
`include "transaction.sv"
`include "generator.sv"
`include "driver.sv"
class environment;
//generator and driver instance
generator gen;
driver driv;
//mailbox handle's
mailbox gen2driv;
//virtual interface
virtual intf vif;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif);
//get the interface from test
this.vif = vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv);
driv = new(vif,gen2driv);
endfunction
//
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen.ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
endtask
//run task
task run;
pre_test();
test();
post_test();
$finish;
endtask
endclass
Test
Test code is written with the program block.
The test is responsible for,
- Creating the environment.
- Configuring the testbench i.e, setting the type and number of transactions to be generated.
- Initiating the stimulus driving.
program test; ---- endprogram
1. Declare and Create an environment,
//declaring environment instance
environment env;
initial begin
//creating environment
env = new(intf);
end
2. Configure the number of transactions to be generated,
//setting the repeat count of generator as 10, means to generate 10 packets
env.gen.repeat_count = 10;
3. Initiating the stimulus driving,
//calling run of env, it interns calls generator and driver main tasks.
env.run();
4. Complete Test Code,
`include "environment.sv"
program test(intf intf);
//declaring environment instance
environment env;
initial begin
//creating environment
env = new(intf);
//setting the repeat count of generator as 10, means to generate 10 packets
env.gen.repeat_count = 10;
//calling run of env, it interns calls generator and driver main tasks.
env.run();
end
endprogram
TestBench Top
- This is the topmost file, which connects the DUT and TestBench.
- TestBench top consists of DUT, Test and Interface instances.
- The interface connects the DUT and TestBench.
module tbench_top; --- endmodule
1. Declare and Generate the clock and reset,
//clock and reset signal declaration
bit clk;
bit reset;
//clock generation
always #5 clk = ~clk;
//reset Generation
initial begin
reset = 1;
#5 reset =0;
end
2. Create Interface instance,
//creatinng instance of interface, in-order to connect DUT and testcase intf intf(clk,reset);
3. Create Design Instance and Connect Interface signals,
//DUT instance, interface signals are connected to the DUT ports
adder DUT (
.clk(i_intf.clk),
.reset(i_intf.reset),
.a(i_intf.a),
.b(i_intf.b),
.valid(i_intf.valid),
.c(i_intf.c)
);
4. Create a test instance and Pass the interface handle,
//Testcase instance, interface handle is passed to test as an argument test t1(intf);
5. Add logic to generate the dump,
initial begin
$dumpfile("dump.vcd"); $dumpvars;
end
6. Complete testbench top code,
`include "interface.sv"
`include "random_test.sv"
module tbench_top;
//clock and reset signal declaration
bit clk;
bit reset;
//clock generation
always #5 clk = ~clk;
//reset Generation
initial begin
reset = 1;
#5 reset =0;
end
//creatinng instance of interface, inorder to connect DUT and testcase
intf i_intf(clk,reset);
//Testcase instance, interface handle is passed to test as an argument
test t1(i_intf);
//DUT instance, interface signals are connected to the DUT ports
adder DUT (
.clk(i_intf.clk),
.reset(i_intf.reset),
.a(i_intf.a),
.b(i_intf.b),
.valid(i_intf.valid),
.c(i_intf.c)
);
//enabling the wave dump
initial begin
$dumpfile("dump.vcd"); $dumpvars;
end
endmodule
SystemVerilog TestBench Example – with Scb
‘ADDER’ TestBench With Monitor and Scoreboard
TestBench Architecture

Only monitor and scoreboard are explained here, Refer to ‘ADDER’ TestBench Without Monitor, Agent, and Scoreboard for other components.
Monitor
- Samples the interface signals and converts the signal level activity to the transaction level.
- Send the sampled transaction to Scoreboard via Mailbox.
- Below are the steps to write a monitor.
1. Writing monitor class.
class monitor; ------ endclass
2. Declare interface and mailbox, Get the interface and mailbox handle through the constructor.
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual intf vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif,mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the interface
this.vif = vif;
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
3. Sampling logic and sending the sampled transaction to the scoreboard.
task main;
forever begin
transaction trans;
trans = new();
@(posedge vif.clk);
wait(vif.valid);
trans.a = vif.a;
trans.b = vif.b;
@(posedge vif.clk);
trans.c = vif.c;
@(posedge vif.clk);
mon2scb.put(trans);
trans.display("[ Monitor ]");
end
endtask
4. Complete monitor code.
class monitor;
//creating virtual interface handle
virtual intf vif;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif,mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the interface
this.vif = vif;
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
//Samples the interface signal and send the sample packet to scoreboard
task main;
forever begin
transaction trans;
trans = new();
@(posedge vif.clk);
wait(vif.valid);
trans.a = vif.a;
trans.b = vif.b;
@(posedge vif.clk);
trans.c = vif.c;
@(posedge vif.clk);
mon2scb.put(trans);
trans.display("[ Monitor ]");
end
endtask
endclass
Scoreboard
Scoreboard receives the sampled packet from the monitor and compare with the expected result, an error will be reported if the comparison results in a mismatch.
class scoreboard; ------ endclass
1. Declaring the mailbox and variable to keep count of transactions, connecting handle through the constructor,
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//constructor
function new(mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
2. logic to compare the received result with the expected result,
Note: As the DUT behavior is simple, a single line is added for generating the expected output.
Complex designs may use the reference model to generate the expected output.
(trans.a+trans.b) == trans.c
//Compares the Actual result with the expected result
task main;
transaction trans;
forever begin
mon2scb.get(trans);
if((trans.a+trans.b) == trans.c)
$display("Result is as Expected");
else
$error("Wrong Result.\n\tExpeced: %0d Actual: %0d",(trans.a+trans.b),trans.c);
no_transactions++;
trans.display("[ Scoreboard ]");
end
endtask
3. Complete scoreboard code.
class scoreboard;
//creating mailbox handle
mailbox mon2scb;
//used to count the number of transactions
int no_transactions;
//constructor
function new(mailbox mon2scb);
//getting the mailbox handles from environment
this.mon2scb = mon2scb;
endfunction
//Compares the Actual result with the expected result
task main;
transaction trans;
forever begin
mon2scb.get(trans);
if((trans.a+trans.b) == trans.c)
$display("Result is as Expected");
else
$error("Wrong Result.\n\tExpeced: %0d Actual: %0d",(trans.a+trans.b),trans.c);
no_transactions++;
trans.display("[ Scoreboard ]");
end
endtask
endclass
Environment
Here only updates are mentioned. i.e adding monitor and scoreboard to the previous example.
1. Declare the handles,
//generator and driver instance generator gen; driver driv; monitor mon; //---NEW CODE--- scoreboard scb; //---NEW CODE--- //mailbox handle's mailbox gen2driv; mailbox mon2scb; //---NEW CODE--- //virtual interface virtual intf vif;
2. In Construct Method, Create
- Mailbox (mon2scb)
- Monitor
- Scoreboard
and pass the interface handle through the new() method.
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif);
//get the interface from test
this.vif = vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
mon2scb = new(); //---NEW CODE---
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv);
driv = new(vif,gen2driv);
mon = new(vif,mon2scb); //---NEW CODE---
scb = new(mon2scb); //---NEW CODE---
endfunction
3. Calling monitor and scoreboard tasks,
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
mon.main(); //---NEW CODE---
scb.main(); //---NEW CODE---
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen.ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions);
wait(gen.repeat_count == scb.no_transactions); //---NEW CODE---
endtask
4. Complete environment class code.
`include "transaction.sv"
`include "generator.sv"
`include "driver.sv"
`include "monitor.sv"
`include "scoreboard.sv"
class environment;
//generator and driver instance
generator gen;
driver driv;
monitor mon;
scoreboard scb;
//mailbox handle's
mailbox gen2driv;
mailbox mon2scb;
//virtual interface
virtual intf vif;
//constructor
function new(virtual intf vif);
//get the interface from test
this.vif = vif;
//creating the mailbox (Same handle will be shared across generator and driver)
gen2driv = new();
mon2scb = new();
//creating generator and driver
gen = new(gen2driv);
driv = new(vif,gen2driv);
mon = new(vif,mon2scb);
scb = new(mon2scb);
endfunction
//
task pre_test();
driv.reset();
endtask
task test();
fork
gen.main();
driv.main();
mon.main();
scb.main();
join_any
endtask
task post_test();
wait(gen.ended.triggered);
wait(gen.repeat_count == driv.no_transactions); //Optional
wait(gen.repeat_count == scb.no_transactions);
endtask
//run task
task run;
pre_test();
test();
post_test();
$finish;
endtask
endclass
Edit and Execute Simple adder TestBench code in EDA Playground.
SystemVerilog TestBench Example — Adder
Let’s Write the SystemVerilog TestBench for the simple design “ADDER”.
Before writing the SystemVerilog TestBench, we will look into the design specification.
ADDER:
Below is the block diagram of ADDER.
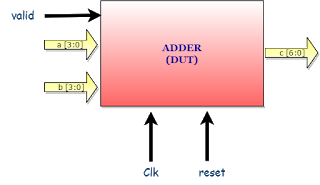
Adder is,
- fed with the inputs clock, reset, a, b and valid.
- has output is c.
The valid signal indicates the valid value on the a and b, On valid signal adder will add the a and b, drives the result in the next clock on c.
Adder add/Sum the 4bit values ‘a’ and ‘b’, and drives the result on c in the next clock.
waveform diagram:
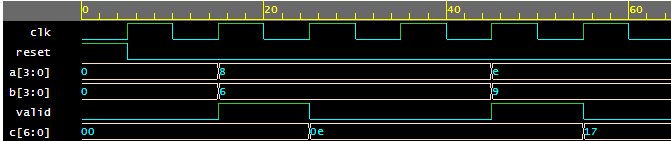
waveform snapshot from EPWave – EDAPlayground
For the simplicity and ease of understanding, let’s write the two TestBecnh’s,
SystemVerilog TestBench
SystemVerilog TestBench Architecture
About TestBench
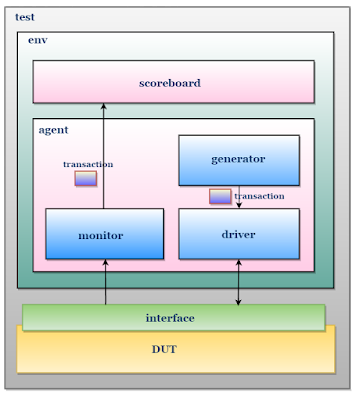
Testbench or Verification Environment is used to check the functional correctness of the Design Under Test (DUT) by generating and driving a predefined input sequence to a design, capturing the design output and comparing with-respect-to expected output.
Verification environment is a group of class’s performing specific operation. i.e, generating stimulus, driving, monitoring, etc. and those classes will be named based on the operation
TestBench Components
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| transaction | class | Defines the pin level activity generated by agent (to drive to DUT through the driver) or the activity has to be observed by agent (Placeholder for the activity monitored by the monitor on DUT signals) |
| generator | class | Generates the stimulus (create and randomize the transaction class) and send it to Driver |
| driver | class | Receives the stimulus (transaction) from a generator and drives the packet level data inside the transaction into pin level (to DUT |
| monitor | class | Observes pin level activity on interface signals and converts into packet level which is sent to the components such as scoreboard |
| agent | class | An agent is a container class, which groups the class’s (generator, driver, and monitor) specific to an interface or protocol |
| scoreboard | class | Receives data items from monitors and compares them with expected values. Expected values can be either golden reference values or generated from the reference model |
| environment | class | The environment is a container class for grouping higher level components like agent’s and scoreboard |
| test | program | The test is responsible for,
|
| testbench_top | class | This is the topmost file, which connects the DUT and TestBench. It consists of DUT, Test and interface instances, the interface connects the DUT and TestBench |
TestBench Hierarchy
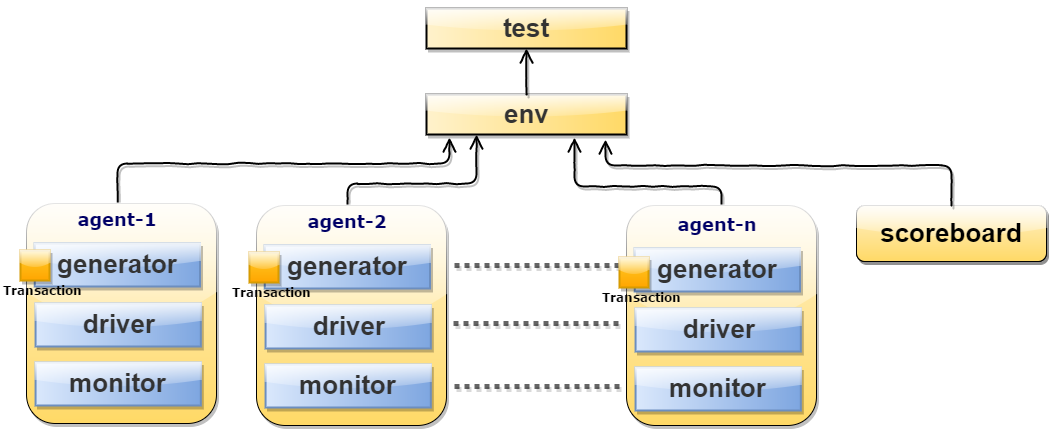
TestBench Architecture

